Polar bears (Ursus maritimus) and tigers (Panthera tigris) are the apex predators—they stand at the top of their food chain. Siberian tiger
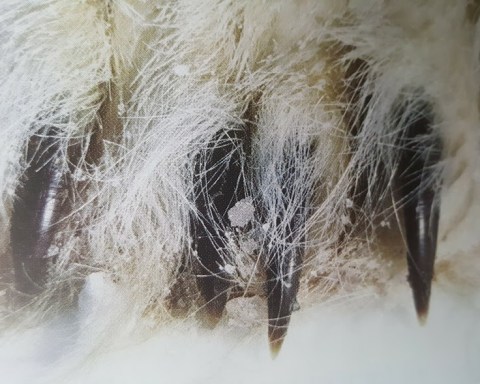
MoreLike all bears, the polar bear has five pointed horny nails on each digit of its foot. The polar bear claws aren’t
MoreGrizzlies are close cousins of polar bears. Although polar bears (Ursus maritimus) are believed to have evolved from grizzly bears (Ursus arctos
MoreIn this article we are going to discuss about polar bear giving birth to its cubs as well as the bear’s birth
MoreWe have gathered some of the most amazing and unbelievable polar bear cubs facts which you probably don’t know. Just to let
MorePolar bears look like a white mammoth-sized animal that navigates through the Arctic sea ice whilst camouflaging into the Arctic snowy background.
MoreDo you know how long do polar bears sleep in a 24-hour day? Well, you will not believe that polar bears sleep
MoreDuring summer, polar bears will spend as much as 7 to 8 hours a day sleeping. But it’s pretty hard to observe
MoreDo you have any idea how many babies do polar bears have at a time? In this article, we’ll try to explain
MorePolar bears are pretty strong swimmers—probably the strongest of all the land-based predators. They will spend much of their time in swimming
More